The Importance of Clear Communication in Taking Medications Correctly
Advertisement
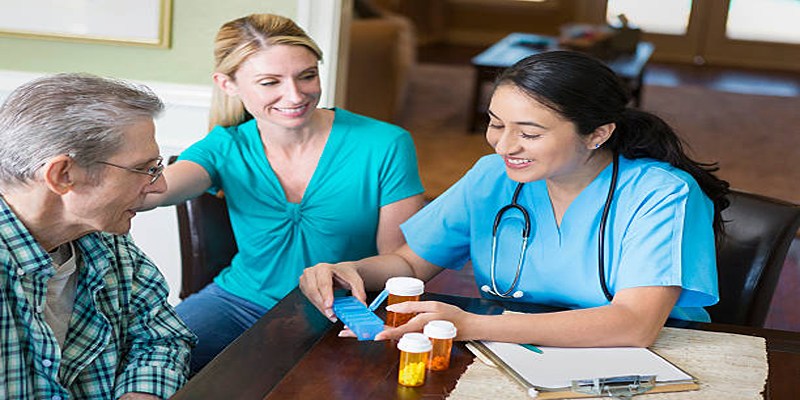
Taking medications correctly is important to achieve their intended effects and maintain good health. Clear communication between health professionals, patients and nurses ensures proper understanding of dosage, time and potential side effects. Incorrect communication can lead to errors or complications, while at the same time the instructions of the drug and highlighting the need for clarity and understanding while promoting successful treatment results.
The Importance of Clear Communication:

Medications are designed to address specific health conditions, but their effectiveness hinges on proper use—correct dosage, timing, and administration. When patients lack a clear understanding of how to take their medications, the risk of mistakes rises. These errors, such as missed doses or incorrect amounts, can undermine treatment and delay recovery.
Clear communication acts as a vital bridge between healthcare providers and patients. It ensures instructions are not only understood but also followed correctly. By fostering clarity, patients are empowered to take an active role in managing their health, mistakes are minimized, and trust in the treatment process is strengthened.
Common Challenges in Medication Communication:
Even with the best intentions, various barriers can disrupt effective communication about medications, putting patients' health and treatment outcomes at risk. Below are some of the most frequent challenges:
1. Complex Medical Terminology
Healthcare professionals often rely on technical or medical terms that may be confusing for patients. Phrases like "take twice daily" or "take with food" might seem clear but are often misinterpreted.
For instance, "twice daily" might be understood as taking two pills at once or mistakenly spaced. Misunderstandings like these can lead to improper medication use, reducing effectiveness or causing unintended side effects.
2. Language and Cultural Barriers
Patients from diverse linguistic and cultural backgrounds may struggle when instructions are not provided in their native language or fail to respect cultural nuances. For example, certain cultural beliefs or practices might make a patient hesitant to take medications as instructed.
Additionally, literal translations of medical advice often fail to capture the intended meaning. Without tailored communication and support, such barriers can result in non-adherence or incorrect use of prescribed treatments.
3. Limited Health Literacy
Health literacy varies widely among patients, and not everyone has the skills to interpret medical terms, read prescription labels accurately, or understand potential side effects. Instructions like "take on an empty stomach" may leave patients unsure about timing or what qualifies as an "empty stomach." Patients with limited health literacy may feel too intimidated to ask questions, leading to errors in medication use or failure to follow treatment plans correctly.
4. Information Overload
During medical appointments, patients often receive an overwhelming amount of information about their conditions, treatment plans, and medications. This overload can make it difficult to retain essential details, such as how and when to take medications or which side effects to monitor. Without reinforcement or reminders, patients may forget or misunderstand these instructions after leaving the healthcare setting.
Strategies to Enhance Communication:
Effective communication between healthcare providers and patients is key to overcoming challenges and ensuring mutual understanding. Here are some practical and impactful strategies:
1. Simplify Language
Healthcare providers should prioritize clarity by avoiding complex medical jargon. Instead, they should use straightforward terms. For instance, rather than saying "administer orally," they can simply say "take by mouth." Visual aids like diagrams and charts can further enhance comprehension.
2. Encourage Open Dialogue
Patients should feel empowered to ask questions about their medications without hesitation. Providers can foster this by creating a supportive, non-judgmental environment. Questions such as "Can you explain that again?" or "What happens if I miss a dose?" should be welcomed and thoroughly addressed.
3. Offer Written Instructions
Since verbal explanations can be easily forgotten, providing written materials—such as pamphlets or printed instructions—gives patients a reliable reference for later use. This is particularly valuable for complex medication schedules or long-term treatments.
4. Practice the Teach-Back Method
The teach-back approach involves asking patients to restate instructions in their own words. This technique allows providers to confirm understanding and quickly address any misconceptions, fostering better retention of information.
5. Integrate Technology
Digital tools, including mobile apps and reminder systems, can significantly improve medication management. These platforms can send dose reminders, offer educational resources, and track adherence, making it easier for patients to stay on top of their treatment plans.
The Patient's Role in Effective Communication:
Clear communication in healthcare is a two-way street. While healthcare providers play a vital role in delivering clear instructions, patients also have an active part to play. Here’s how you can contribute to ensuring effective communication:
- Ask Questions Without Hesitation: If something isn’t clear, don’t hesitate to ask questions or seek clarification. It’s always better to address uncertainties upfront than risk misunderstandings that could lead to mistakes in your care.
- Be Transparent About Your Medical History: Provide a full and honest account of your medical history, including any allergies, current medications, and pre-existing conditions. This transparency helps your healthcare provider prevent harmful interactions and personalize your treatment plan.
- Stay Proactive with Regular Check-Ins: Consistently follow up with your healthcare provider to share updates on concerns, side effects, or progress. Regular communication ensures your treatment remains effective and any potential issues are resolved quickly.
The Role of Clear Communication in Better Health Outcomes:

Effective communication goes beyond ensuring patients take their medications correctly—it empowers them to manage their health with confidence. Clear guidance improves treatment adherence, reduces errors, and enhances patient satisfaction, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
1. Enhanced Treatment Adherence
Clear and straightforward instructions empower patients to fully understand their treatment plans, reducing confusion and making it easier to follow through with medications, lifestyle changes, or therapy schedules. This consistency not only leads to better health outcomes but also gives patients a greater sense of control over their healthcare journey.
2. Reduced Risk of Medication Errors
Precise and detailed communication plays a crucial role in minimizing errors, such as incorrect dosages, missed doses, or improper medication use. This is especially vital for complex treatment regimens, medications with strict dosing requirements, or drugs that carry the risk of serious side effects if used incorrectly.
3. Improved Patient Satisfaction
When patients clearly understand their treatment plans and feel supported by their healthcare providers, they become more confident and engaged in their care. This understanding fosters trust, strengthens the patient-provider relationship, and creates a sense of being valued. Satisfied patients are more likely to provide positive feedback, adhere to recommendations, and remain actively involved in their care, ultimately leading to a more positive healthcare experience.
Conclusion:
Clear communication is essential for safe and effective medication use. It empowers patients to understand their treatment plans, minimizes the risk of errors, and improves health outcomes. Healthcare providers can bridge the gap between knowledge and action by using simple, accessible language, encouraging open dialogue, and employing tools like written instructions and teach-back techniques. Patients also play a crucial role by actively participating in discussions, sharing their medical history, and seeking clarification when needed.
On this page
The Importance of Clear Communication: Common Challenges in Medication Communication: 1. Complex Medical Terminology 2. Language and Cultural Barriers 3. Limited Health Literacy 4. Information Overload Strategies to Enhance Communication: 1. Simplify Language 2. Encourage Open Dialogue 3. Offer Written Instructions 4. Practice the Teach-Back Method 5. Integrate Technology The Patient's Role in Effective Communication: The Role of Clear Communication in Better Health Outcomes: 1. Enhanced Treatment Adherence 2. Reduced Risk of Medication Errors 3. Improved Patient Satisfaction Conclusion:Advertisement