Angioplasty or Surgery: Best Treatment for Left Main Artery Disease
Advertisement
Individuals that suffer from left main artery disease need swift and successful medical intervention for this critical heart disease. People typically choose between surgical procedures and angioplasty to regain heart blood flow. The selection between these treatments bases on patient-specific features combined with their associated risks as well as anticipated long-term results. The selection of these life-saving options requires full understanding of the choices by patients.
Understanding Left Main Artery Disease:
The left main coronary artery plays a vital role in heart health, branching into the left anterior descending and circumflex arteries to deliver oxygen-rich blood to the heart's left side. When this artery gets clogged or narrowed by plaque buildup (atherosclerosis), it can seriously cut off blood flow—leading to chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or even heart failure.
The condition named Left main artery disease (LMAD) presents especially dangerous risks because it affects major areas of heart tissue. Preventive care starts with timely diagnosis along with intervention which aims to stop deadly heart complications from happening. The evaluation of left main artery disease severity depends on cardiologists using diagnostic instruments including coronary angiography and stress tests along with advanced imaging techniques to create suitable treatment strategies.
Treatment Options for Left Main Artery Disease (LMAD):
When it comes to managing Left Main Artery Disease (LMAD), two primary treatment options are available:
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) with Angioplasty
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) Surgery
Both approaches aim to restore proper blood flow to the heart, but they differ significantly in method, invasiveness, and long-term outcomes. Below, we delve into each option to help you better understand their benefits and limitations.
1. Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) with Angioplasty
Angioplasty, or PCI, is a minimally invasive procedure designed to open blocked arteries. A catheter with a small balloon is inserted into the affected artery, and the balloon is inflated to compress the plaque and widen the artery. In most cases, a stent (a small mesh tube) is also placed to keep the artery open and maintain blood flow.
Advantages of PCI:
- Minimally Invasive: Performed through a small incision, typically in the wrist or groin, PCI involves less risk and a shorter recovery period compared to surgery.
- Quicker Recovery: Patients can often resume normal activities within days.
- Suitable for High-Risk Patients: An ideal option for those who may not tolerate surgery due to advanced age, comorbidities, or other health conditions.
Limitations of PCI:
- Risk of Restenosis: In some cases, the treated artery may narrow again over time, necessitating repeat procedures.
- Less Effective for Complex Cases: PCI may not be suitable for patients with multiple or extensive blockages or particularly challenging artery anatomy.
- Variable Long-Term Outcomes: While effective in many cases, PCI may not offer the same durability as surgery for certain patients.
2. Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) Surgery
CABG is a surgical procedure that takes a healthy blood vessel from another part of your body to create a new pathway around a blocked artery. Think of it as building a detour to help blood flow freely to your heart, keeping it strong and healthy.
Advantages of CABG:
- Long-Lasting Results: CABG provides durable symptom relief and reduces the risk of future heart attacks, often outperforming PCI in long-term effectiveness.
- Ideal for Complex Cases: The preferred choice for patients with multiple blockages or particularly intricate coronary anatomy.
- Comprehensive Approach: CABG can address several blocked arteries in a single procedure.
Limitations of CABG:
- Invasive Nature: As an open-heart surgery, CABG carries a higher risk of complications, including infection, bleeding, or stroke.
- Extended Recovery Time: Patients typically require several weeks to fully recover and resume daily activities.
- Not Suitable for Everyone: Patients with severe comorbidities or advanced age may face higher surgical risks and may not be ideal candidates.
Choosing Between Angioplasty and Surgery
When deciding between angioplasty and coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), several key factors must be considered:
1. Severity of the Condition
For patients with severe blockages in multiple arteries or complex anatomical issues, CABG often provides a more comprehensive and durable solution. This surgical option is particularly effective for those with advanced coronary artery disease or conditions like diabetes, where multiple bypasses may be needed to restore optimal blood flow.
2. Overall Health
A patient’s overall health plays a significant role in determining the best approach. Factors such as age, physical fitness, and pre-existing conditions like diabetes or kidney disease influence the choice. Younger, healthier individuals may recover more quickly from surgery, while older patients or those with significant comorbidities might benefit from the less invasive nature of angioplasty, which places less strain on the body.
3. Risk of Complications
Angioplasty is often the safer option for high-risk patients due to its minimally invasive nature, shorter recovery time, and lower immediate risk of complications. However, for patients who are healthy enough to undergo surgery, CABG may offer more favorable long-term outcomes, particularly in complex cases.
4. Patient Preferences
Personal preferences are crucial in the decision-making process. Patients who value a faster recovery and less downtime may lean toward angioplasty, while those seeking long-term benefits and durability might opt for CABG, even if it involves a more invasive procedure and a longer recovery period.
Advances in Treatment Options:
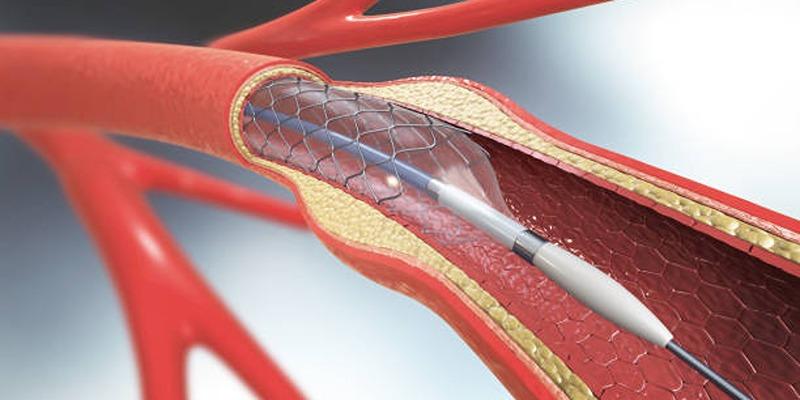
Medical advancements have significantly improved the safety and efficacy of both angioplasty and coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery. Here are some key innovations shaping modern cardiovascular care:
1. Drug-Eluting Stents
Drug-eluting stents represent a breakthrough in angioplasty. These stents are coated with medication that is gradually released into the arterial walls, reducing the risk of restenosis (re-narrowing of blood vessels) after the procedure. By minimizing the chances of recurring blockages, drug-eluting stents have greatly enhanced the long-term success rates of angioplasty and are now a cornerstone of contemporary cardiovascular treatments.
2. Minimally Invasive CABG
Coronary artery bypass grafting has been revolutionized by minimally invasive techniques. Unlike traditional open-heart surgery, these methods involve smaller incisions, leading to shorter hospital stays, faster recovery, reduced pain, and fewer complications. This patient-friendly approach makes CABG a safer and more accessible option for many individuals needing bypass surgery.
3. Hybrid Procedures
For complex cases where a single treatment may not suffice, hybrid procedures offer a tailored solution. By combining angioplasty with surgical intervention, such as placing drug-eluting stents and performing bypass surgery in a single session, these techniques leverage the strengths of both approaches. Hybrid procedures provide a comprehensive treatment plan for patients with severe or multi-vessel coronary artery disease, improving outcomes and delivering more personalized care.
Conclusion:
Left Main Artery Disease (LMAD) is a serious condition that requires prompt and effective treatment. Angioplasty and CABG surgery are both viable options, each with its own advantages and limitations. Choosing the best approach should be a collaborative decision with a cardiologist, carefully considering the patient’s medical history, overall health, and individual preferences. Angioplasty offers a less invasive solution with faster recovery, while CABG surgery often provides more durable results, especially in complex cases.
On this page
Understanding Left Main Artery Disease: Treatment Options for Left Main Artery Disease (LMAD): 1. Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) with Angioplasty 2. Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) Surgery Choosing Between Angioplasty and Surgery 1. Severity of the Condition 2. Overall Health 3. Risk of Complications 4. Patient Preferences Advances in Treatment Options: 1. Drug-Eluting Stents 2. Minimally Invasive CABG 3. Hybrid Procedures Conclusion:Advertisement